If you follow Windows 10 development at all, you’ve probably heard this “Hardware accelerated GPU scheduling” buzzword that’s been going around since last year. At that point, Hardware-accelerated GPU scheduling was little more than just an option in Settings, but after driver update, the setting is now functional.
If you want to try out the new feature and see if it makes a difference to your apps or games, you would first need to check that you’re running Windows 10 version 2004 or Build 19041 in Settings > System > About.
After upgrading to Windows 10 May 2020 Update, you would need to download Nvidia GeForce 451.48+ or Adrenalin 2020 Edition 20.5.1 Beta driver. While the Nvidia GeForce 451.48 enables GPU scheduling support for everyone, AMD has currently limited the availability of its new driver to beta testers.
Once you’ve got the latest version of Windows 10 and drivers, you can turn on or off the feature using Settings and Windows Registry.
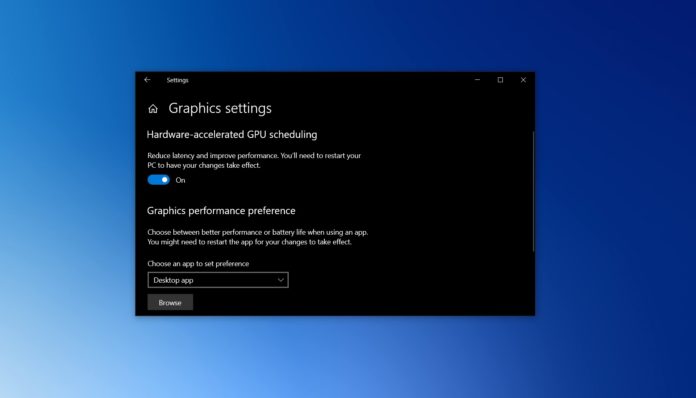
Turn On or Off Hardware Accelerated GPU Scheduling in Settings
To enable hardware accelerated GPU scheduling on Windows 10, use these steps:
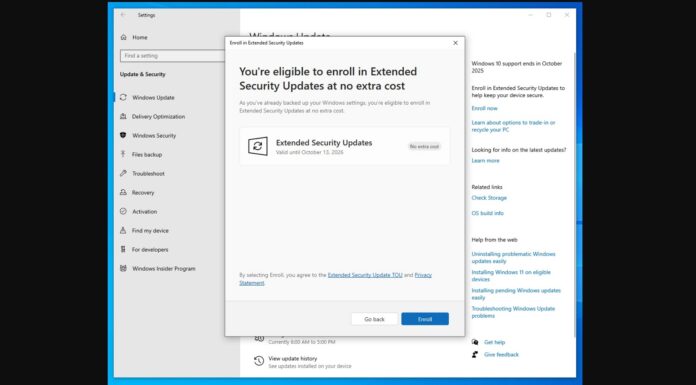
- Open Start Menu and tap on Settings cog icon.
- In Settings, click on ‘System’ and open ‘Display’ tab.
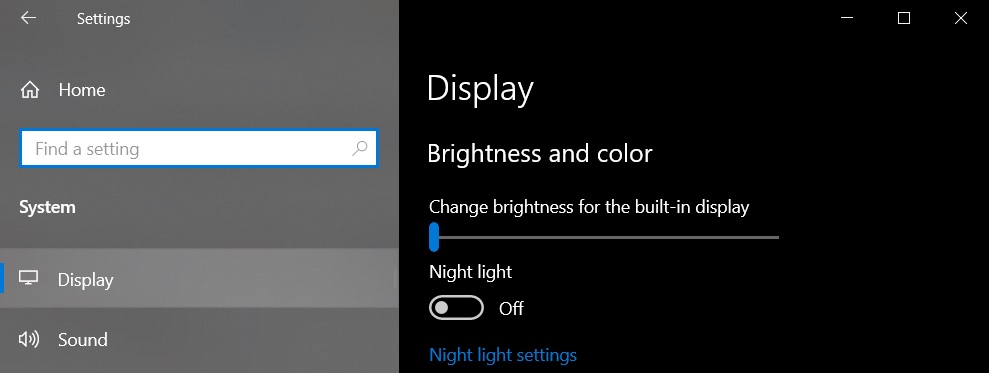
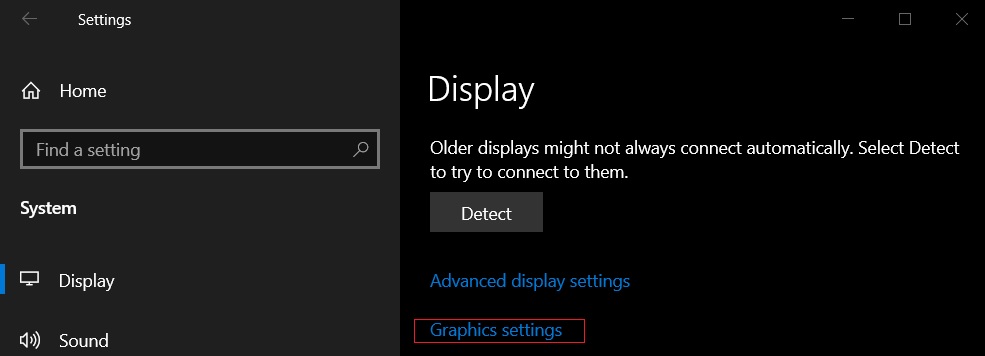
- Under the “Multiple Displays” section, select “Graphics settings”.
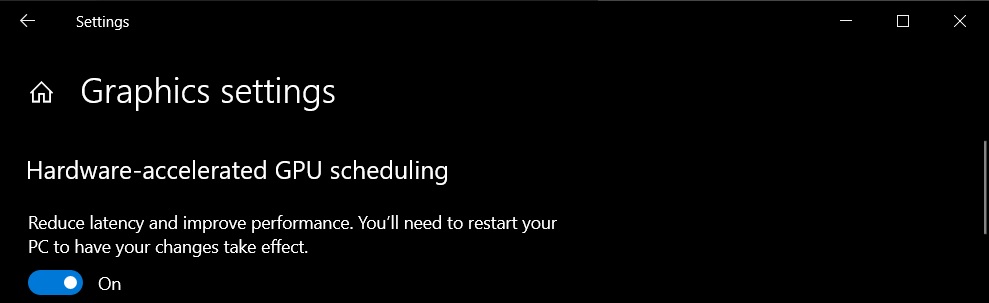
- Turn on or off “Hardware-accelerated GPU scheduling” option.
- Restart the system.
Enable Hardware Accelerated GPU Scheduling using Registry
To force hardware accelerated GPU scheduling on Windows 10, use these steps:
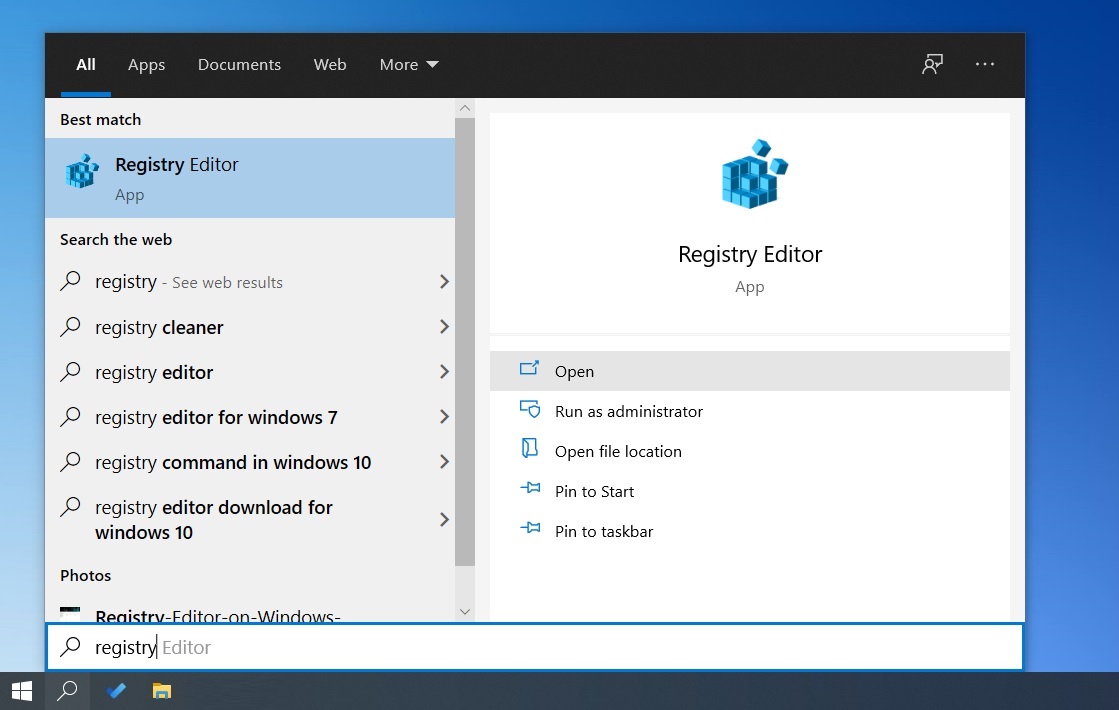
- Open Windows Search.
- Search for ‘Registry’ and select the first option.
- In Registry editor, navigate to ‘HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\GraphicsDrivers’.
- Locate DWORD tiled “HwSchMode”. Use value 2 to turn it On and 1 to turn it Off.
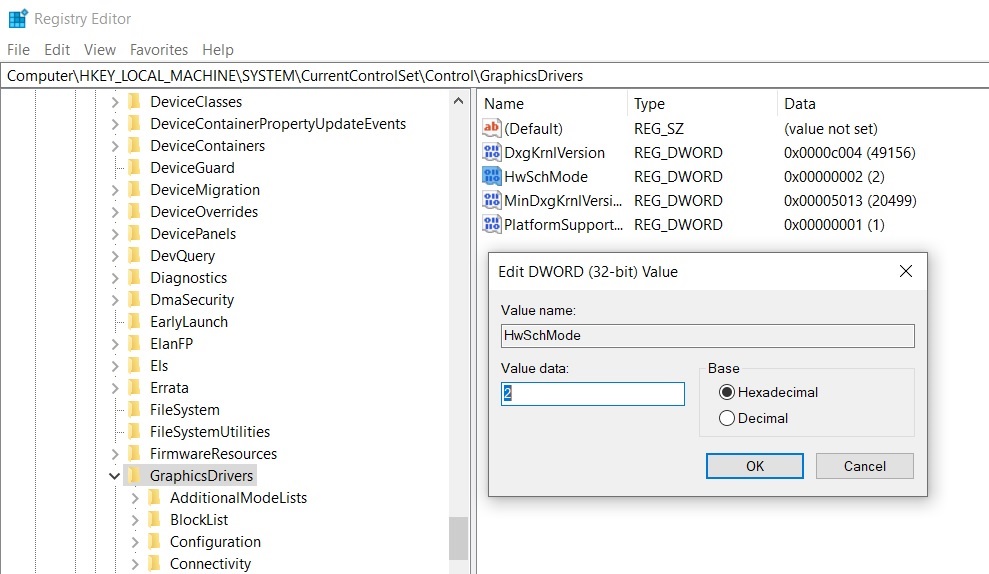
- Restart the system.
- Open Settings > Display > Graphics settings and toggle the option.
- Restart the system.
Understanding the hardware accelerated GPU scheduling feature
Long story short, hardware accelerated GPU scheduling feature in Windows 10 represents a fundamental redesign in how Windows Display Driver Model (WDDM) works. While Microsoft says users won’t see any significant changes after activating it now, some believe that the feature will eventually reduce input lag on low-end and mid-core processors.
In theory, Windows 10 hardware accelerated GPU scheduling feature passes most GPU scheduling tasks to a dedicated GPU-based scheduling processor, which should free up the CPU a little and can potentially result in a small input lag improvement.