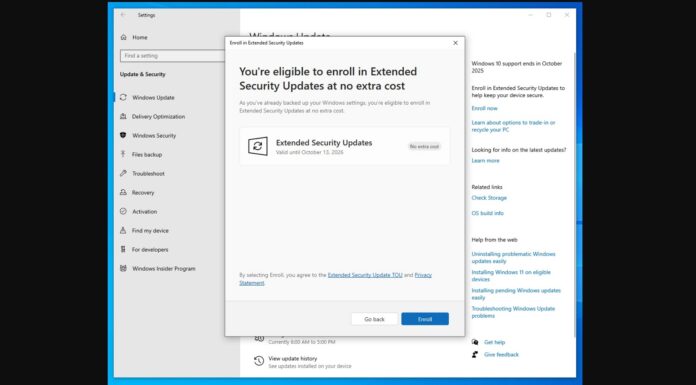
Microsoft is testing multiple new features for Windows 10 and the last preview build introduced a few big changes, including the ability to update Paint through the Microsoft Store. In the preview builds, another noticeable change is a new option under the power menu that let apps be restarted when you sign out and back in again.
For those unaware, some apps (mostly UWP) have the ability to register for restart. This is useful when you want to get back to what you were doing after rebooting the system. In Windows 10 version 21H1 or older, this option is tied to Windows Settings app.
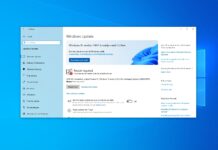
With Windows 10’s Sun Valley update, Microsoft is adding that option to the power menu, which can be accessed via the Start Menu. As shown in the screenshot below, the new option “Restart apps” will appear under Sleep, Shutdown and Restart. When enabled, Windows will save your restartable apps and restore them the next time you sign in.
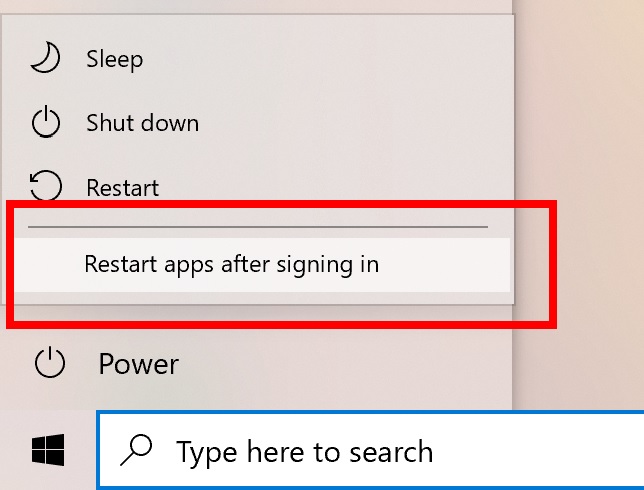
Windows 10 will automatically restart any of those apps that are restartable when you reboot the system without closing any apps and login after reboot.
As noted, it’s a feature that you can already enable in Windows 10 version 20H1 via Settings > Accounts > Sign-in options > Restart apps.
Windows Tools integration
Microsoft is also introducing a new “Windows Tools” folder in File Explorer to replace the “Administrative Tools” and organize advanced administrator tools for power users.
The administrative Tools page in Control Panel has included all versions of Windows 10 and it is a collective name for advanced tools in the OS. The hub, which is now being renamed to “Windows Tools”, will include shortcuts to advanced apps, such as Command Prompt, Windows Disk Cleanup, PowerShell, Registry Editor, Group Policy and more.
Currently, you can access over 40 apps from the Windows Tools folder.
The shortcut to the Windows Tools folder is available in the Start Menu, but since it’s a Control Panel applet, it can also be accessed via Control Panel. In addition to Control Panel, users can also access the feature by entering the command “control admintools” in Command Prompt / PowerShell.
Windows Tools panel is a successor to Administrative Tools and it’s likely that future Windows Updates will introduce additional tools.