Windows computers are pre-formatted to NTFS, including storage drives in laptops, external hard drives and USB sticks. Microsoft could be planning to bring ReFS (a new file system) to replace NTFS on specific systems, according to references spotted in the latest Windows 11 preview build.
Before we discuss the new ReFS file system, we need to understand what NTFS is. The NT File System (NTFS) was developed by Microsoft in 1992, and it can be used on systems that have licenses.
NTFS is proprietary and is the default file system of Windows 11, Windows 10 or older. It stores or organises files on a hard disk or external hard drive. To better understand how NTFS works, let’s look at its process: a disk is formatted and divided into partitions, and Windows tracks every file stored in the system.
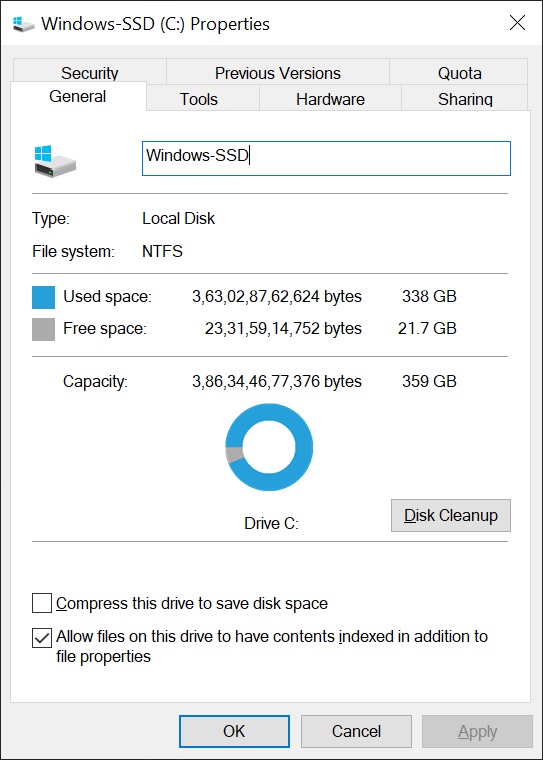
You can check your file system by going to “This PC” and right-clicking on any drive, preferably the Windows drive. You’ll notice “NTFS” next to the file system, as shown in the below screenshot from our Windows 10 device. The results are similar on Windows 11 PCs too.
Windows 11’s latest preview builds include support for ReFS, the Resilient File System, which is Microsoft’s newest file system, and it’s currently used in Windows Servers. Unlike NTFS, ReFS is significantly better in data availability and scalability.
As per Microsoft’s documentation, “it is designed to maximize data availability, scale efficiently to large data sets across diverse workloads, and provide data integrity with resiliency to corruption”.
The Resilient File System is better than NTFS in many ways, including storage and future innovation. For example, NTFS supports a maximum of 256 terabytes. On the other hand, this new file system offers support for up 35 petabytes. The difference is vast when considering the conversion factor – a petabyte equals 1024 terabytes.
We don’t know if this feature could mean the end of NTFS, but there’s a possibility that some Windows 11 Enterprise or Business computers will ship with ReFS as the default file system.
That’s because several advantages of ReFS will favour enterprises and professionals, including a feature that converts expensive physical file copy operations to quick logical ones. Another feature improves performance and reduces I/O.
Other features include mirror-accelerated parity, file-level snapshots and better security.
However, ReFS isn’t as good as it may appear on paper. It doesn’t have features currently supported by NTFS, including system compression and encryption support. Support for disk quotas and removable media is also missing from ReFS, which makes it a deal breaker for consumer PCs.
ReFS support in Windows 11 is a work in progress
Microsoft is still working on ReFS support for Windows 11, and it looks like it won’t be ready for consumers anytime soon.
We could see ReFS as the default file system on some new hardware by the end of the year, but Microsoft’s plans are always subject to change.